FOAM FIRE EXTINGUISHERS (Chemical Foam) 9 LITRES

9 LITRES FOAM FIRE EXTINGUISHERS (Chemical Foam)
Foam is an effective smothering agent, used for liquid fires mainly. It acts by flowing over the liquid fuel oil surface and isolating the fire from the air, also prevents re-ignition due to the foam stability. Usually the foams are of i. Protein Based ii. Synthetic
Picture Credit: Reed’s Volume 8
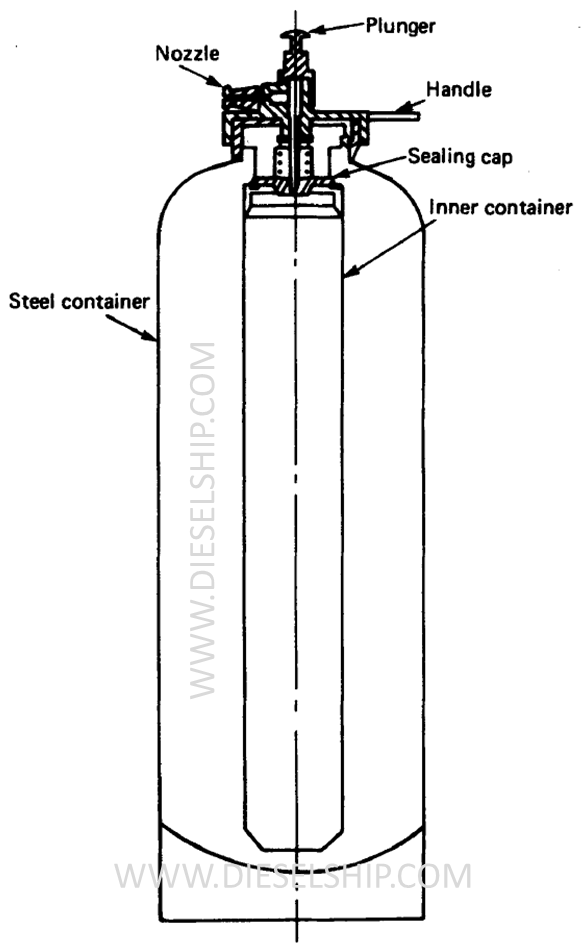
- The main container is filled with sodium bicarbonate solution and a long inner polythene container is filled with aluminium sulphate. The inner container is sealed by a cap held in place by a plunger. When the plunger is unlocked by turning it, the cap is released. The extinguisher is then inverted for the two liquids to mix. Carbon dioxide is produced by the reaction which pressurises the container and forces out the foam.
Al2 (SO4)3 + 6 NaHCO3 -> 2Al (OH) 3 + 3Na2SO4 + 6 Co2
- The chemicals react to form Co2 which serves as propellant, but the action is slower, giving time for bubbles to form. Foam-making substances added to the sodium carbonate determine the nature of the foam formed. The ratio of the foam produced to liquid is in the order of 8:1 to 12:1.
- Because the extinguisher has to be inverted for operation, no internal pipe is fitted. When being recharged the cap seal should be examined and the pressure relief holes in the rim checked. The chemical foam extinguisher may be slow.
Construction Details
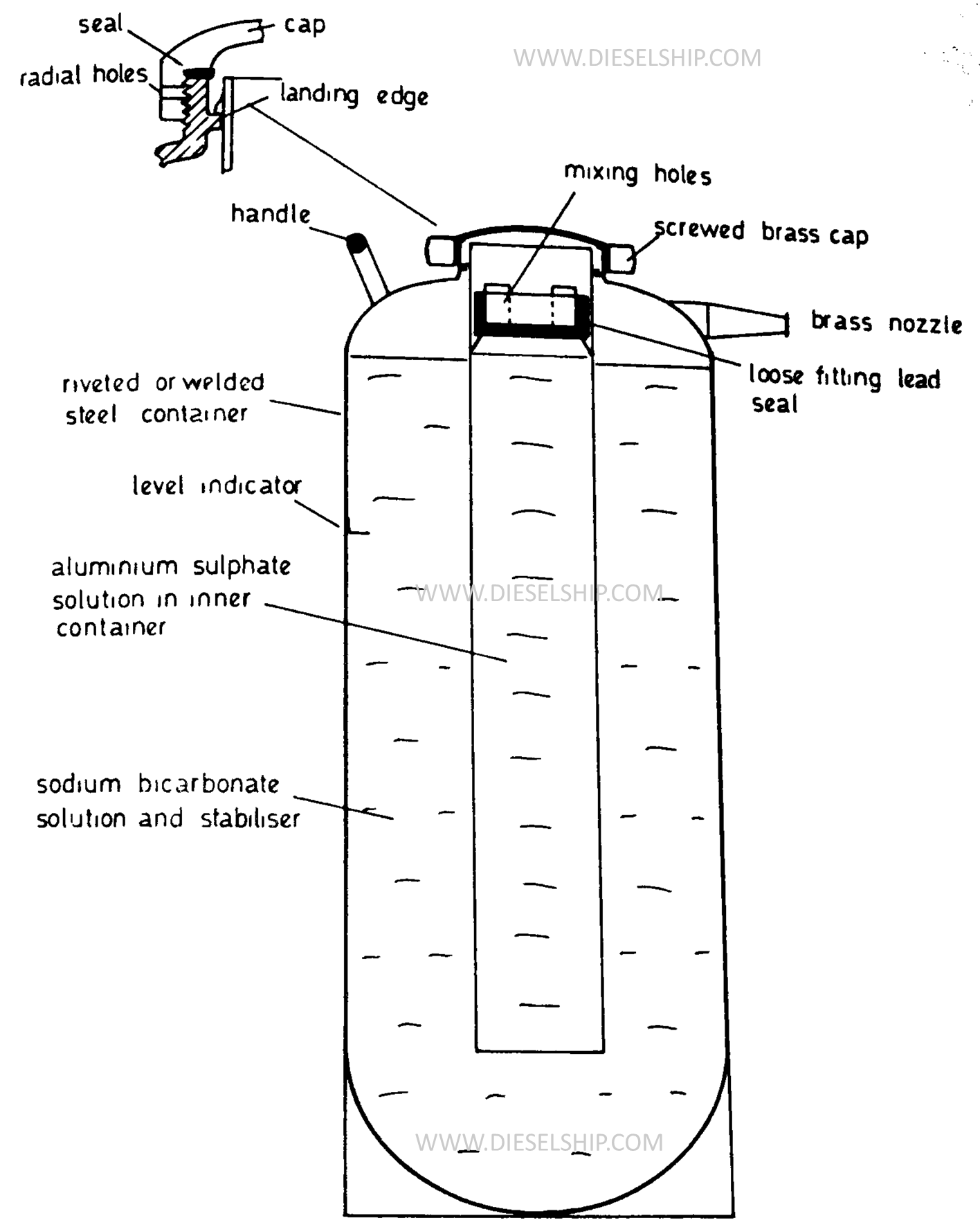
- A 9 litre portable foam fire extinguisher of the inverting type as shown in both the pictures above. The inner and outer containers are made of lead or zinc coated steel. The outer containers is of riveted construction.
- Cap and nozzle is made of brass and a loosely fitting lead valve may be situated at the top of the inner container to provide a seal. The brass cap has a series of small radial holes drilled trough it which communicate the inside of the extinguisher with the atmosphere when the cap is being unscrewed, hence these holes serve as a vent if the nozzle is blocked.
Internal Contents of the Extinguisher
- The inner container is filled with a solution of aluminium sulphate and the annular space formed by the inner and outer container is filled upto the level indicator with a solution of sodium bi carbonate and foam stabilizer.
- Proportions of solutions approximately 1:3 inner and outer containers respectively, total solutions volume is 9 litres.
How to operate the Chemical foam Extinguisher
- Operation of the chemical foam extinguisher is different from that of other portable extinguishers.
- The extinguisher is inverted, the lead seal falls, clearing the ports in the inner container and the two solutions can then freely mix. When these solution mixes, the above shown reaction takes place producing Co2 which drives the foam out with enough pressure.
Performance expected on a portable Co2 Extinguisher
- Range: The injection range is usually 7.5 to 9 meters.
- Duration : the duration of exhalation is usually about 90 seconds
- Quantity: 72 litres of foam at a pressure of 7 bar is produced.
- Testing : The extinguisher is tested at 25 bar pressure.
Picture Credit: Introduction to marine engg by TA Taylor
| General Requirement for Portable Fire Extinguishers – FSS CODE
? The quantity of powder or co2 extinguisher shall be of at least of 5 kg and foam extinguisher have a capacity at least of 9ltr, mass of all portable fire extinguishers shall not exceed 23 kg and this shall have a capability at least to that of 9 ltr fluid extinguisher. ? Recharging of the fire extinguisher shall be of approved type. ? Portable foam applicator unit shall consist of a foam nozzle (inductor type) connected to a fire main via fire hose together with portable tank containing at least 20 ltr of foam forming liquid and one spare tank for foam making liquid and the nozzle shall be capable of producing foam suitable for extinguishing an oil fire at the rate at least 1.5 m3/min.
|
Bibliography: Reeds volume 8, Introduction to marine engineering, HD Mc George book & FSS Code