Mate’s Receipt

Mate’s Receipt
What is a Mate’s Receipt ?
- A Mate’s receipt (MR) is a receipt issued and signed by the chief mate of the ship for goods received on board. MR is nowadays replaced by a modern document called the Standard Shipping Note (SSN), but can still be seen in conventional trade like general cargo, dry bulk or tanker.
- The information in both the MR should be identical to that of the B/L. the MR should be completed from the ship’s tally and show the actual quantity and condition of the cargo as received. When the condition of cargo justifies it, the M/R should be remarked as ‘torn bags’, ‘stained bales’ or ‘rust drums’ etc.
- Should there be a difference in the tally of the ship and the shipper, MR should reflect the smaller of the two figures with the remark that “X more bales in dispute, if onboard to be delivered”, X being the difference in the tally figures.
- MR is normally on a shipowner’s format and made in triplicate. The original is given to the shipper, the 2nd given to the agent and the 3rd left in the book of MR to be referred toat the time of issuance of the B/L. M/R is not a document of title.
Primafacie evidence
MR is a receipt issued by the Commanding Officer of the ship when the cargo is loaded on the ship. It is a prima facie evidence that goods are loaded in the vessel. Mate’s receipt is first handed over to the Port Trust Authorities. After making payment of all port dues, the exporter or his agent collects the mate’s receipt from the Port Trust Authorities. Mate’s receipt is freely transferable. It must be handed over to the shipping company in order to get the bill of lading. Bill of lading is prepared on the basis of the mate’s receipt.
MR is not a document of title of goods. It is merely a receipt of goods. However, it is an important document as without it, the exporter will not be able to obtain the title document of goods, i.e., the bill of lading.
Types of Mate’s Receipts:
(a) Clean Mate’s Receipt: The Commanding Officer of the ship issues a clean MR, if he is satisfied that goods are packed properly and there is no defect in the packing of the cargo or package.
(b) Qualified Mate’s Receipt: A qualified MR is issued when the Commanding Officer of the ship is not satisfied with the packing of the goods and the shipping company does not take any responsibility of damage in transit.
Contents of Mate’s Receipt:
(a) Name and logo of the shipping line.
(b) Name and address of the shipper.
(c) Name and the number of vessel.
(d) Name of the port of loading.
(e) Name of the port of discharge and place of delivery.
(f) Marks and container number.
(g) Packing and container description.
(h) Total number of containers and packages.
(I) Description of goods in terms of quantity.
(i) Container status and seal number.
(k) Gross weight in kg. and volume in terms of cubic metres.
(I) Shipping bill number and date.
(m) Signature and initials of the Chief Officer.
Significance of Mate’s Receipt:
(a) It is an acknowledgement of goods received for export on board the ship.
(b) It is a transferable document. It must be handed over to the shipping company in order to get the bill of lading.
(c) Bill of lading, which is the title of goods, is prepared on the basis of the mate’s receipt.
(d) it enables the exporter to clear port trust dues to the Port Trust Authorities.
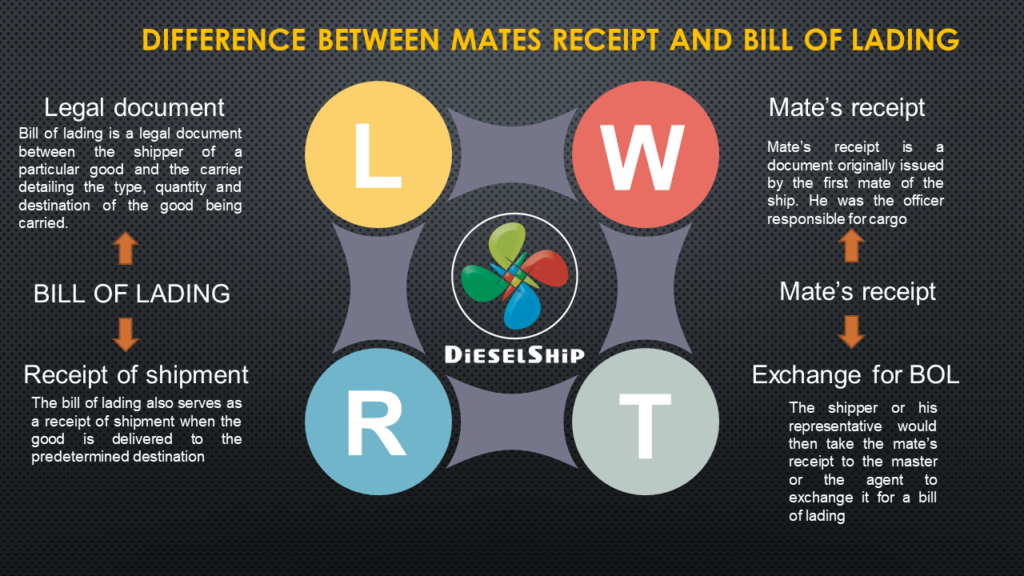
How is it different from Bill of lading?
Check here to learn Difference Between Mates Receipt And Bill Of Lading