BOILER BASICS AND TYPES OF BOILERS

Boiler basics and types of boilers | Common issues found on Boiler feed water | Boiler water treatment fundamentals | Water Treatment Philosophy and Overview |Boiler Water Treatments and its purpose
BOILER BASICS AND TYPES OF BOILERS – WATER TUBE BOILER AND FIRE TUBE BOILER
What is a boiler?
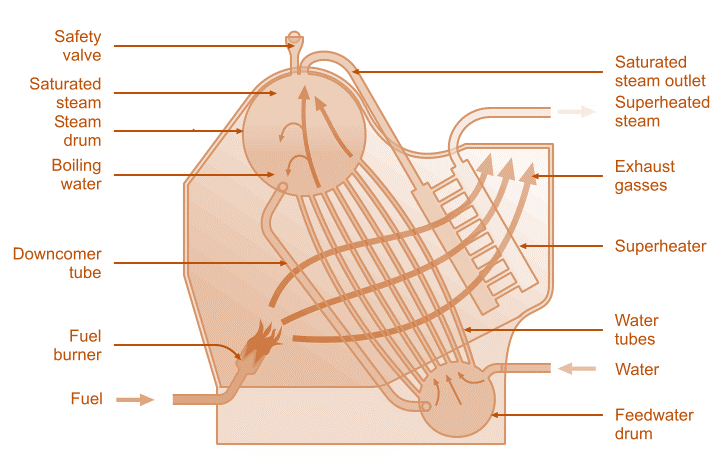
- A boiler is a steel pressure vessel in which water under pressure is converted into steam by the application of combustion. In other words, it is simply a heat exchanger which uses radiant heat and hot flue gases, liberated from burning fuel, to generate steam and hot water for heating and processing loads.
TYPES OF BOILERS
- There are two types:
- Fire tube boilers
- water tube boilers.
SIX MAIN BASIC PARTS
1) Burner
2) Combustion space
3) Convection section
4) Stack
5) Air fans
6) Controls and accessories
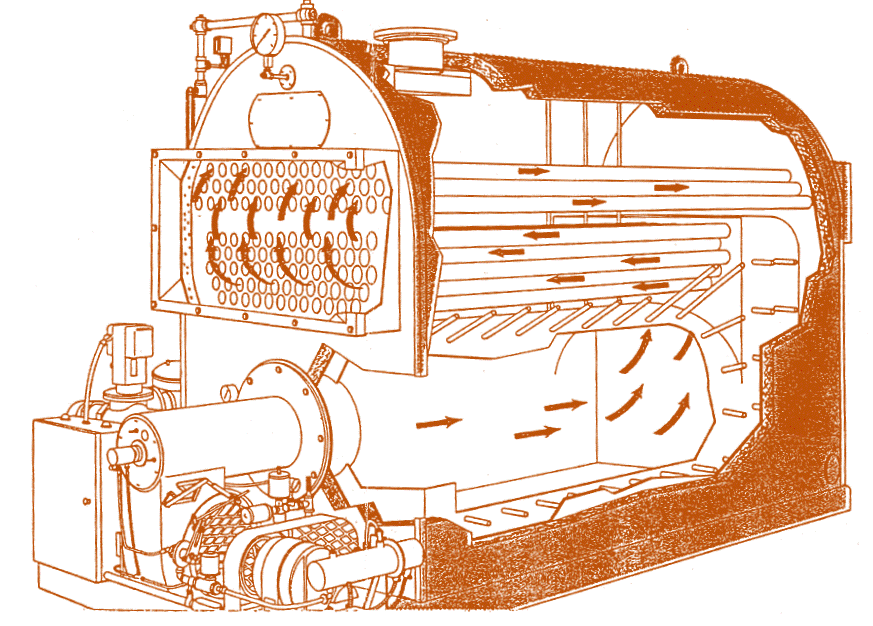
FIRE TUBE BOILER
Hot flue gases flow inside tubes that are submerged in water within a shell.
• Pressures up to about 10 bar
• Produce up to 14 tonnes of steam/hr
• Can meet wide and sudden load fluctuations because of large water volumes
• Usually rated in HP
Wet back designs
- Have a water wall at the back of the boiler in the area where combustion gases reverse direction to enter tubes.
Dry back designs
- Refractory is used at the back, instead of a water wall. Internal maintenance is simplified, but refractory replacement is expensive and overheating, gauging and cracking of tube ends at the entrance to return gas passages often cause problems.
Advantages:
• Lower initial cost
• Few controls
• Simple operation
Disadvantages:
• Drums exposed to heat, increasing the risk of explosion
• Large water volume, resulting in poor circulation
• Limited steam pressure and evaporation
WATER TUBE BOILER
Water flows through tubes that are surrounded by hot combustion gases in a shell.
• Usually rated in tons of steam/hr
• Used for H.P. steam
• High capacity
- In recent years, interest has been revived in high temperature hot water heating systems for institutional, industrial and commercial plants. By increasing the temperature and pressure of the hot water and increasing the size of the generators,
- some advantages are gained over the low pressure steam heating systems previously used. In other cases, special forced circulation boilers have been designed, which consist of many rows of tubes without a steam drum. In another type, heat is supplied by steam from a standard type of boiler which heats the water in a direct contact heater. This is referred to as a cascade system.
Advantages:
• Rapid heat transmission
• Fast reaction to steam demand
• High efficiency
• Safer than firetube boilers
Disadvantages:
• More control than fire tube boilers
• Higher initial cost
• More complicated to operate